Why Is It getting Hard for me Lose Weight?
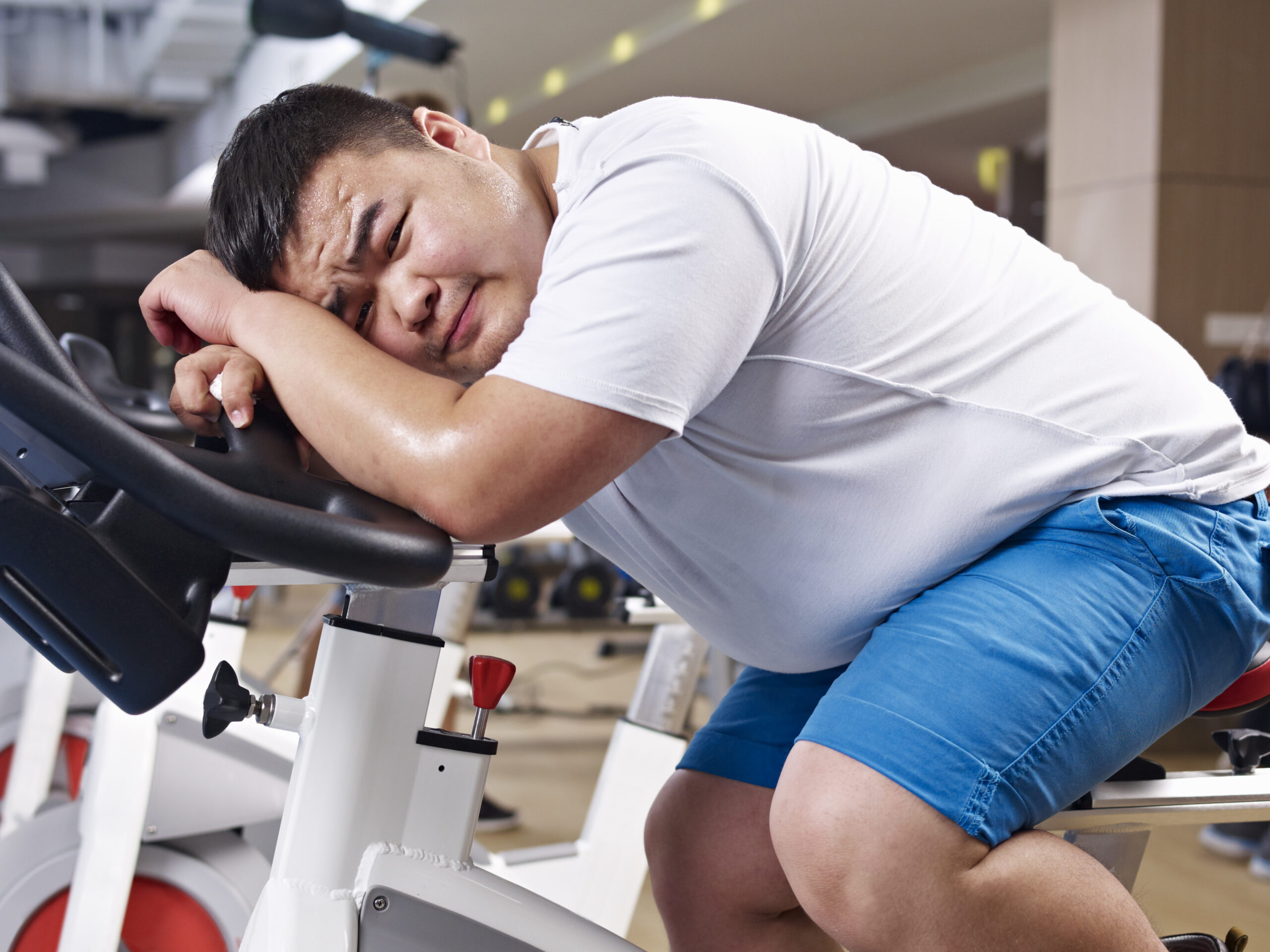
Losing weight is challenging due to a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors that often make sustained weight loss a complex goal.
From metabolic adaptation to hormonal influences, our bodies are wired to resist significant weight loss, a response developed for survival in times of food scarcity. Today, our biology still reacts as if calories were scarce, slowing metabolism and increasing hunger when we cut back on food. Combined with lifestyle habits, emotional stress, and food choices that are highly processed and calorie-dense, many people struggle to lose weight despite their efforts.
Biological Barriers to losing weight
One major barrier to weight loss is our body’s metabolic adaptation. When you reduce calories to lose weight, your metabolism can slow down as a response, burning fewer calories to conserve energy—a phenomenon known as “adaptive thermogenesis.” This adaptation, along with hormone fluctuations, such as increases in the hunger hormone ghrelin and reductions in leptin (the hormone that signals fullness), can lead to increased cravings and a reduced feeling of satisfaction after meals .
Psychological Barriers and Habits
Psychological factors also play a significant role. Emotional eating, stress, and habits ingrained over time can derail weight-loss efforts. Studies show that stress can lead to cravings for high-calorie, sugary foods, often called “comfort foods,” making it difficult to stick to a calorie deficit. Additionally, unhealthy eating habits, like consuming large portions or frequent snacking on processed foods, can work against even the most dedicated weight-loss goals.
Environmental and Societal Influences
The environment in which we live further complicates weight loss. Fast food, high-calorie snacks, and sugary drinks are readily available and often more affordable than healthier options. Our increasingly sedentary lifestyle, fueled by desk jobs and digital entertainment, means people generally expend less energy daily. Additionally, cultural and social events often revolve around food, making it easy to consume more calories than planned.
The Role of Genetics in weight Loss
Genetics also contribute to weight loss difficulty, affecting everything from metabolism to where the body stores fat. Some people are naturally predisposed to hold onto weight more than others, and these genetic factors can influence how quickly someone might gain or lose weight compared to others.
Effective Strategies for Sustainable Weight Loss
Despite these challenges, weight loss is achievable with a focus on sustainable, realistic changes. Incorporating regular physical activity, prioritizing whole foods, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are foundational steps. Additionally, tracking food intake, setting realistic goals, and seeking support—whether through a health professional or community—can make a positive difference in overcoming the biological and environmental barriers to weight loss.